MSU community members must always adhere to MSU’s established acceptable use and institutional data policies and specific types of data should be handled in different ways when using a generative AI product. Please refer to the table below to determine which data types are suitable for each tool.
MSU Guidelines for the Use of Generative Artificial Intelligence (Generative AI) Tools
The MSU Guidelines for the Use of Generative Artificial Intelligence (Generative AI) Tools serve as the overarching authority for institutional, academic, and research uses of AI. Find the official university guidelines at ai.msu.edu/guidelines.
MSU Standards on Data Uses with AI
These standards establish clear expectations for the responsible and secure use of generative AI tools when handling Michigan State University (MSU) data. They complement the MSU Guidelines for the Use of Generative Artificial Intelligence (Generative AI) Tools.
AI Tool Review
Only AI platforms that have been formally evaluated and recommended by MSU IT Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) may be used with institutional data.
No AI tools should be assumed safe for confidential or regulated data unless explicitly approved. Users must also follow any unit-specific or departmental guidance in addition to these IT standards.
AI Use and Data Standards
All use of AI tools, including those provided by vendors through MSU accounts or those found on the approved software list, must comply with
- MSU Institutional Data Policy
- MSU Acceptable Use Policy
- Federal and state law and regulations (e.g., FERPA, HIPAA, ITAR, EAR)
Unless an AI tool is explicitly covered by a formal enterprise agreement with MSU that guarantees privacy and data protection, users should assume that only public data should be considered for use with that tool.
Users must understand the potential data risks and limitations associated with these technologies. These standards outline appropriate data-handling practices, required approvals, and current best practices for safeguarding university and personal information. Additionally, in accordance with FOIA, any records MSU community members produce or retain—including those created through digital collaboration or automated transcription tools—may be subject to public disclosure.
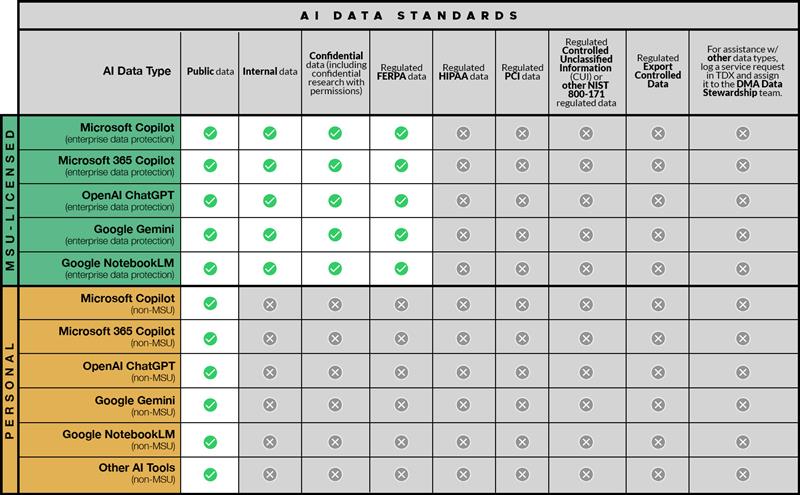
Specific expectations by data type are as follows (note that terms like “input” and “inputting”, below, are assumed to cover both the underlying data provided to the AI tool and any queries, prompts, or other inputs):
- Public data: AI tools may process publicly available, non-sensitive information and general academic concepts. Uses must comply with MSU policy and be reviewed for ethical and reputational impact.
- Confidential and Internal data: Do not input confidential data or internal data, including but not limited to, Social Security numbers, student records, contact details, name/image/likeness, payment card data, or other regulated information, into any AI system without documented approval from MSU IT GRC and written consent from all necessary parties.
- Research data: Researchers must assess the sensitivity of data prior to use. Confidential, proprietary, or human subjects’ data must not be entered into AI tools unless appropriately anonymized and approved by MSU IT GRC with written consent from required stakeholders.
- Intellectual property: Avoid inputting proprietary or unpublished research, internal university documents, or other material protected by intellectual property rights into AI tools without express written consent from all stakeholders.
- Regulated FERPA data: Do not use AI tools to process, store, or transmit any data classified as FERPA.
- Regulated HIPAA data: Do not use AI tools to process, store, or transmit any data classified as ePHI (HIPAA).
- Regulated PCI data: Do not use AI tools to process, store, or transmit any data classified as PCI.
- Regulated ITAR, EAR, and CUI compliance: Do not use AI tools to process, store, or transmit any data classified under International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR), Export Administration Regulations (EAR), or Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI). Improper handling of such data may result in serious legal and compliance consequences.
- Other types of data: For assistance with other data types, submit a service request and assign it to the DMA Data Stewardship team.
Additional Risks and Limitations of Generative AI
Users must remain aware that AI systems present ongoing risks and limitations, including:
- Misinformation and inaccuracies: AI-generated content may be incorrect or outdated. Always verify facts before use.
- Bias and unintentional harm: AI models can reflect or amplify bias in their training data; outputs must be critically reviewed.
- Inappropriate content: AI tools may occasionally produce or respond to content that is inaccurate, inappropriate, or unethical.
- Algorithmic inference: AI systems can infer data patterns beyond intended inputs, potentially exposing sensitive or biased outcomes.
Recommended Practices
For all users of generative AI tools:
- Consider carefully: Evaluate the data you intend to input and the implications for privacy, compliance, and accuracy. Once data is entered into an AI tool, it cannot be retracted.
- Think critically: Independently verify AI-generated results using reliable sources or subject matter experts.
- Understand expectations: Confirm disclosure or citation requirements before submitting or publishing work supported by AI tools.
- Exercise caution: Treat all unvetted AI tools and new software features as unapproved unless explicitly communicated otherwise by MSU IT.
- Stay informed: Follow ongoing university communications for updates on approved AI tools, evolving standards, and new risks.
Questions and Reporting
Questions about these standards or requests for approval of new AI tools should be directed to MSU Information Security at its.infosec.team@msu.edu.


